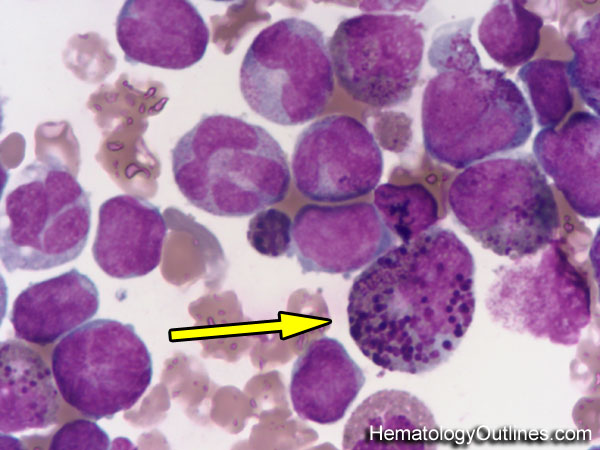
Blood/Blood Cells and Cellular Components ›› Eosinophils and Basophils ›› Abnormal
Dysplastic Eosinophil*
 Click Here for Full Size Click Here for Full Size
Additional Image 1
 › Microscopic Features:- 2-3x larger than a mature RBC
- Low nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (more cytoplasm than nucleus)
- Nucleus is mature and usually with 2 lobes connected by thin chromatin filament (some have 1 lobe or more than 2 lobes)
- Nucleoli are absent
- More cytoplasm with Abnormal secondary granules (usually darker in color resembling basophilic granules)
- The granules are heterogenous and vacuoules may occasionally be noted as well
 › Normal % blood-PB, marrow-BM, lymphoid tissue-LN:- PB: None
- BM: None
- LN: None
 › May Resemble:
 › Differential Diagnoses:
Associated with:
Certain AMLs such as AML with Inv 16 or t(16;16)
Certain Myeloproliferative neoplasms
Certain Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
 › Classic Immunophenotype:- CD45dim+
- High SSC (Side light scatter)
- CD13dim+
- CD16-
- CD15dim+
- (May have some immunophenotypic variability compared to normal eosinophils)
 › Cartoon Image:
 Click and drag
Click and drag

for direct comparison › Misc:- AML with inv16 or t(16;16) was also known as AML-M4Eo (which stood for an AML with monocytic differentiation and Abnormal Eosinophils)
|